Cholesterol lowering drugs Internal Medicine ,Pharmacology ,Prevention
Cholesterol treatment guidlines:
Current guidelines for cholesterol treatment: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/cholesterol/profmats.htm
Drug Treatment:
There are four major classes of medications are used to treat hyperlipidemia:
o HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins)
o Bile acid sequestrants (cholestyramine, cholestipol)
o Nicotinic acid
o Fibric acids
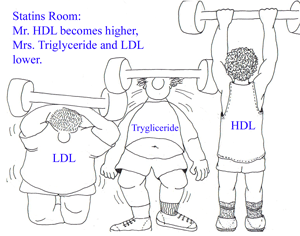
o The statins can lower LDL levels by 18% to 55% and triglyceride levels by 7% to 30%. They also can raise HDL levels by 5% to 15%.Their major side effects include myopathy and an elevation of liver enzyme levels.
o The bile acid resins (cholestyramine, cholestipol) lower LDL levels by 15% to 30%, and raise HDL levels by 3% to 5%. They have no effect on triglyceride levels. Their major side effects include gastrointestinal distress, constipation, and a decrease in the absorption of other drugs.
o Nicotinic acid lowers LDL levels by 5% to 25% and triglyceride levels by 20% to 50%. Nicotinic acid also raises HDL levels by 15% to 35%. The major side effects of nicotinic acid include flushing, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, GI distress, and hepatotoxicity.
o Fibric acids lower LDL levels by 5% to 20% and triglyceride levels by 20% to 50%, and raise HDL levels by 10% to 20%. Their major side effects include dyspepsia, gallstones, myopathy, and unexplained noncardiac death.
- Anatomy
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Dermatology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Gastroenterology
- Geriatric Medicine
- Gynecology
- HIV
- Hematology and Oncology
- Infectious Disease
- Internal Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstetrics
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pediatrics
- Pharmacology
- Prevention
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Rheumatology
- Surgery
- Urology
- case report
- trial reference




